What Is a Carding Attack?
A carding attack is a form of credit card fraud in which cybercriminals use automated bots to verify stolen card details. The goal isn’t to buy expensive goods immediately. Instead, attackers test whether card numbers, expiration dates, CVV codes, and billing details are valid. Once verified, the data is resold or used for large fraudulent purchases elsewhere.

How Carding Bots Work
1. Data Acquisition
Attackers obtain card data from breaches, phishing, malware, or dark web markets. Often, critical fields like CVV or expiration dates are missing.
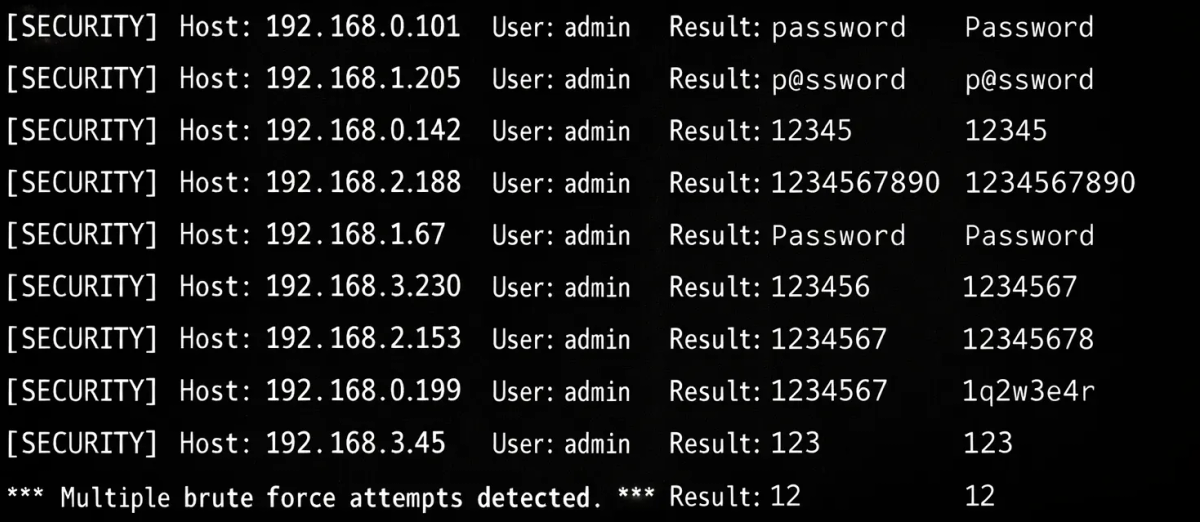
2. Automated Brute-Force Testing
Bots target checkout pages or payment APIs, rapidly cycling through combinations to guess missing fields. This is a classic brute-force pattern, optimized with automation.
3. Validation via Microtransactions
Small-dollar transactions are submitted to observe processor responses. A successful authorization confirms the card is active.
4. Evasion Techniques
To bypass defenses, bots rotate IPs, spoof user agents, distribute requests, mimic human timing, and create fake accounts.
5. Monetization
Validated cards are bundled and sold, or used to purchase resellable goods and gift cards—amplifying fraud across ecosystems.
Why Traditional Defenses Alone Are Not Enough
Firewalls and basic fraud rules are necessary, but insufficient on their own. Carding bots are designed to look like real users. Without a way to reliably distinguish humans from automation, attackers can slip through technical gaps and overwhelm operational teams.
That’s why a layered approach is required.
Proven Strategies to Prevent Carding Attacks
Technical Controls
Bot Protection with Modern CAPTCHA
Because carding is automated, bot protection is the most critical layer. Modern CAPTCHA solutions don’t rely on distorted text or image puzzles. Instead, they silently verify whether traffic originates from real users.
A well-implemented CAPTCHA stops carding bots before they reach payment validation, reducing processor costs and fraud exposure.
Rate Limiting
Limit payment attempts, account creations, and authorization requests per IP, device, or session. This reduces brute-force velocity.
IP Geolocation & Anomaly Detection
Compare IP origin with billing regions and flag high-risk mismatches. Sudden spikes from risky locations often signal carding activity.
Strong Authentication
Use CVV/CVC checks, AVS, and protocols like 3-D Secure where appropriate. These controls increase attacker cost and failure rates.
Operational Controls
Fraud Policies & Purchase Rules
Set thresholds for failed authorizations, microtransactions, and order values—especially for new or unverified accounts.
Monitoring Decline Patterns
Watch for:
- Sudden increases in declined payments
- Bursts of low-value transactions
- Spikes in CVV or AVS failures
- Off-hours activity anomalies
Early detection dramatically reduces losses.
Collaboration with Payment Processors
Processors often detect fraud patterns across merchants. Sharing signals improves response time and prevention accuracy.
Why CAPTCHA Is Essential to Prevent Carding Attacks
Carding attacks depend on scale. Bots can submit thousands of transactions per minute—humans cannot. CAPTCHA breaks this advantage by introducing a verification step that is trivial for real users but prohibitively expensive for bots.
However, not all CAPTCHA solutions are equal.
TrustCaptcha: A Modern CAPTCHA Built to Stop Carding Bots
Proof of Work: Blocking Automation at Scale
TrustCaptcha uses cryptographic proof-of-work challenges that run invisibly in the user’s browser. Real users complete them instantly. Bots, however, cannot solve them efficiently at scale—making mass card testing economically unviable.
This stops carding attempts before payment validation begins.
Bot Score: Adaptive Risk-Based Protection
Every interaction is evaluated with a bot score based on technical signals and request behavior. As risk increases, TrustCaptcha automatically increases challenge difficulty—without impacting legitimate users.
This dynamic scaling is critical during attack spikes.
Invisible by Design
No image grids. No puzzles. No interruptions. Legitimate customers never notice TrustCaptcha, preserving conversion rates and user experience.
Privacy-First Architecture
TrustCaptcha does not rely on cookies, fingerprinting, or behavioral tracking. No personal data is harvested—making it suitable for privacy-sensitive environments and regulatory compliance.
Accessible and Inclusive
Because it doesn’t test “humanness” through visual challenges, TrustCaptcha works seamlessly with assistive technologies and supports accessible experiences.
How TrustCaptcha Fits into a Layered Defense
TrustCaptcha works best as the first line of defense, stopping bots early so that rate limits are less likely to trigger false positives, fraud rules remain accurate, payment processors see cleaner traffic, and chargebacks and penalties decrease.
Combined with authentication, monitoring, and operational controls, it significantly strengthens your ability to prevent carding attacks.
Conclusion: Stay Ahead of Carding Attacks
Carding attacks continue to evolve in speed and sophistication. For IT professionals and buyers, the question is no longer if you’ll be targeted—but when. A proactive, layered strategy is essential.
By combining operational discipline with modern bot protection, organizations can dramatically reduce fraud risk. CAPTCHA remains a cornerstone of this strategy—and TrustCaptcha shows that security, privacy, and user experience don’t have to be trade-offs.
Try TrustCaptcha Free
Ready to see the difference for yourself? 👉 Try TrustCaptcha for free and protect your checkout, APIs, and payment flows from carding bots—without friction or privacy compromises.