Context: The Expanding Risk Around Digital Access
Digital access has become the primary attack surface for modern organizations. Cloud platforms, SaaS tools, APIs, and remote workforces have dramatically increased the number of identities and access points that security teams must protect. As a result, identity and access management has moved from a back-office IT function to a frontline security priority.
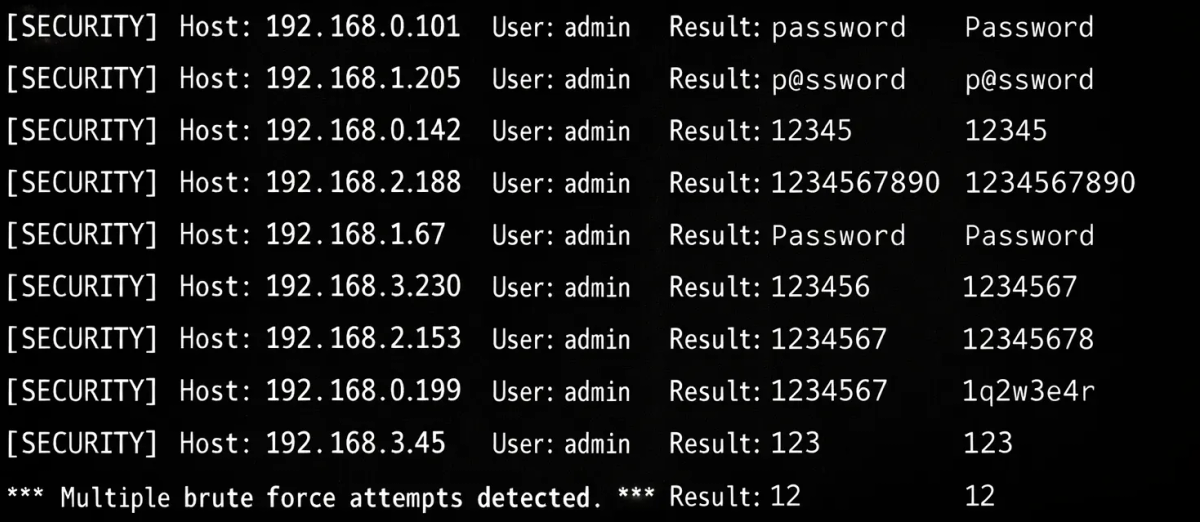
Every employee login, customer signup, and privileged admin session represents a potential entry point for attackers. Weak IAM security leads to account takeovers, data breaches, regulatory violations, and loss of customer trust. This is why modern organizations view identity as the new security perimeter.
Identity and access management security provides the foundation for controlling access across workforce, customer, and machine identities. However, traditional IAM alone is no longer enough. Automated attacks, bots, and abuse require additional protective layers, especially at authentication and authorization endpoints.
Identity and Access Management (IAM): Core Concepts and Identity Types
What is Identity and Access Management?
Identity and access management governs how digital identities are created, managed, authenticated, and authorized across systems and applications. It combines ID management with access control to enforce security policies consistently.
At its core, IAM security ensures:
- Only legitimate users gain access
- Access aligns with business roles and risk
- Actions are logged, auditable, and compliant
IAM is central to Zero Trust strategies, regulatory compliance, and modern cybersecurity architectures. Without strong IAM security, even the best perimeter defenses can be bypassed.
Identity Management and Access Control
Identity Management (ID Management)
Identity management controls the full identity lifecycle:
- Provisioning new users and service accounts
- Modifying access as roles change
- Deprovisioning access when identities are no longer required
Poor ID management leads to orphaned accounts, excessive permissions, and unnecessary risk. These gaps expand the attack surface and undermine access management security.
Access Control
Access control determines who can access which resources and under what conditions. Common models include:
- RBAC (Role-Based Access Control)
- ABAC (Attribute-Based Access Control)
- Least-Privilege Enforcement
Modern environments require continuous evaluation of access decisions, not just one-time authentication.
Privileged Identity Management (PIM)
Privileged identity management focuses on securing accounts with elevated permissions, such as system administrators and service accounts. These identities are high-value targets for attackers.
Key PIM risks include:
- Standing privileges that never expire
- Credential theft and misuse
- Lack of session visibility
Best practices for IAM security include:
- Just-in-time privileged access
- Approval-based workflows
- Privileged session monitoring and auditing
Customer Identity and Access Management (CIAM)
CIAM secures identities for customers, partners, and external users. Unlike workforce IAM, CIAM environments face:
- Massive identity volumes
- Public-facing authentication endpoints
- High expectations for frictionless user experience
CIAM security challenges include:
- Account takeover attacks
- Fake account creation
- Bot-driven abuse of login and registration flows
Balancing usability with strong IAM security is critical for customer trust and revenue protection.
IAM Security: Threat Landscape and Security Controls
IAM Security Threat Landscape
| Threat | Description |
|---|---|
| Credential Stuffing | Reused leaked credentials |
| Brute-Force Attacks | Automated password guessing |
| Bot Abuse | Automated login and signup attacks |
| Privilege Escalation | Excessive or misconfigured access |
| Insider Threats | Misuse of legitimate access |
| Regulatory Gaps | Weak access auditing |
These threats highlight why access management security must extend beyond credentials alone.
Strengthening IAM Security with Layered Controls
Effective IAM security uses multiple, reinforcing controls:
| Security Control | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Multi-Factor Authentication | Reduces credential theft risk |
| Risk-Based Authentication | Adjusts security dynamically |
| Continuous Monitoring | Detects abnormal access |
| Least-Privilege Enforcement | Limits breach impact |
| Bot Mitigation | Stops automated abuse |
CAPTCHA as a Critical IAM Security Control
Traditional IAM defenses cannot fully stop automated attacks. Bots can bypass passwords, rotate IPs, and simulate human behavior. This is why CAPTCHA has become essential for IAM security, particularly in CIAM and privileged access portals.
CAPTCHA protects:
- Login endpoints
- Registration flows
- Password reset processes
Low-friction CAPTCHA is especially important in CIAM environments where user experience matters. When implemented correctly, CAPTCHA adds security without harming conversion rates.
Modern CAPTCHA for IAM: TrustCaptcha
TrustCaptcha is designed specifically to strengthen identity and access management security without frustrating legitimate users.
How TrustCaptcha Enhances IAM Security
TrustCaptcha protects IAM and CIAM endpoints using two advanced mechanisms:
1. Proof of Work (PoW)
TrustCaptcha requires clients to perform computational work that is trivial for humans but costly at scale for bots. This:
- Slows down automated attacks
- Makes credential stuffing and brute-force attacks economically unviable
- Protects login, signup, and password reset flows
2. Bot Score Intelligence
TrustCaptcha continuously evaluates behavioral signals to assign a bot score to each request. This enables:
- Risk-based enforcement of access control
- Seamless user experiences for legitimate users
- Strong defenses against automation
Why TrustCaptcha Fits Modern IAM and CIAM
- Protects public-facing authentication endpoints
- Integrates seamlessly with access control workflows
- Preserves user experience while reducing fraud
- Ideal for CIAM platforms, privileged access portals, and high-risk authentication events
By stopping bots before authentication logic is abused, TrustCaptcha reinforces IAM security at its most vulnerable points.
Conclusion: Building Resilient Access Management Security
Modern organizations must integrate identity and access management, privileged identity management, CIAM, and bot mitigation into a single, layered strategy.
IAM security must evolve to address automation-driven threats. CAPTCHA is no longer a usability tradeoff; when implemented correctly, it is a powerful enabler of secure, scalable access.
TrustCaptcha delivers this balance, protecting identities, preserving user experience, and strengthening access control across modern digital ecosystems.
Next steps
Strengthen your identity and access management security today.
👉 Try TrustCaptcha for free and see how proof-of-work and bot scoring protect your IAM and CIAM environments in real time.